Kafka data cleaning middleware helps Python web scraping systems move raw data through a reliable pipeline while you clean, validate, and normalize it. Instead of letting crawlers and cleaners depend on each other directly, Kafka buffers the data stream and lets each component scale independently. As a result, your scraping architecture becomes more stable, easier to maintain, and easier to scale.
In this article, you will learn how Kafka supports data cleaning in scraping systems, how a topic-based workflow looks, and how to run a simple producer–consumer pipeline with Docker and Python.
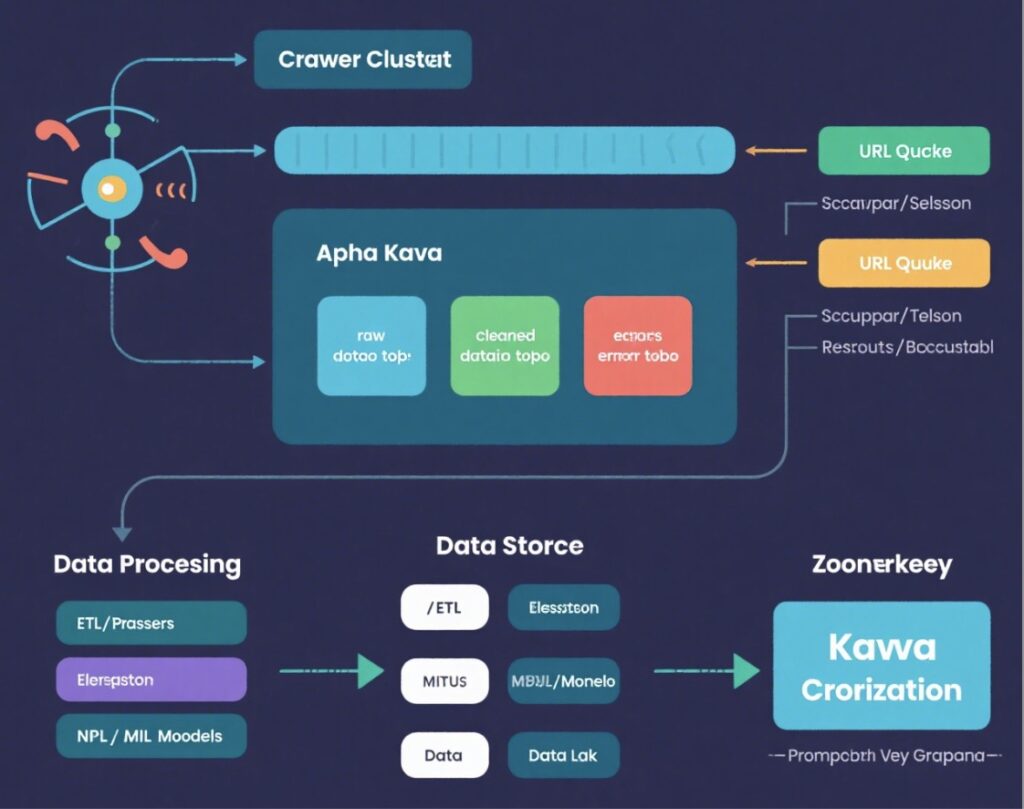
Why Kafka fits web scraping and data cleaning
Think of Kafka as an “intelligent transfer station” between two teams:
- Scraper cluster: fetches pages and emits raw HTML or JSON.
- Cleaning services: parse, filter noise, normalize formats, validate fields, and redact sensitive content.
Without Kafka, scrapers often push data straight into a cleaner or database. However, when cleaning slows down or fails, the whole pipeline stalls. With Kafka data cleaning middleware, scrapers keep producing messages, while Kafka absorbs traffic spikes and delivers messages to cleaners when they are ready.
I. Core Roles of Kafka in Web Scraping Architecture
1) Decouple crawling and cleaning
Scrapers produce raw data to Kafka topics. Meanwhile, cleaners consume messages and output structured results. Therefore, you can change the cleaning logic without touching crawler code (and vice versa).
2) Buffer traffic and enable async processing
When crawling runs faster than cleaning, Kafka stores messages. As a result, scrapers continue crawling instead of waiting.
3) Scale horizontally with consumer groups
Kafka consumer groups let you run multiple cleaner instances in parallel. In addition, you can increase throughput by adding more consumers without redesigning the pipeline.
II.Core goals of data cleaning in scraping pipelines
- Removing Noise Data
- Filter out useless information such as HTML tags, advertising content, and null values.
- Example: Text extracted from web pages may contain
<script>tags or line breaks.
- Format Standardization
- Unify time formats, currency units, encoding methods, etc.
- Example: Convert
January 1, 2023to2023-01-01.
- Data Validation and Correction
- Verify data integrity (e.g., whether required fields are missing).
- Fix obvious errors (e.g., phone number formats, email addresses).
- Sensitive Information Desensitization
- Mask sensitive data such as ID numbers and phone numbers.
III. Collaborative Workflow of Kafka and Data Cleaning
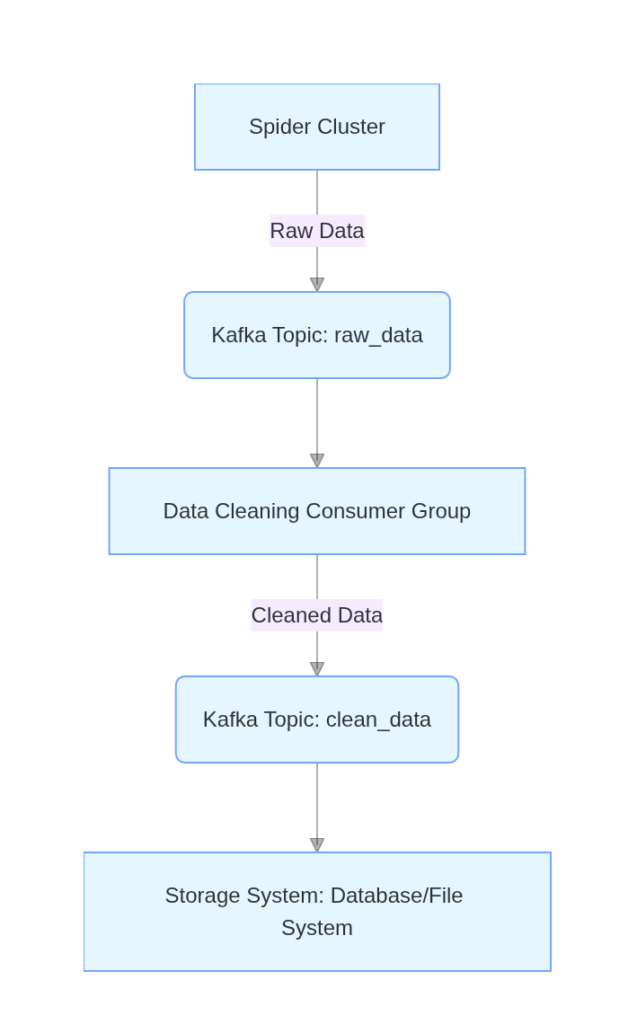
Installation
Since Kafka has many dependencies, this tutorial uses Docker for installation, which is convenient and time-saving. (Prerequisite: Docker is installed on the machine)
First, install ZooKeeper
docker run -d \
--name zookeeper \
-p 2181:2181 \
-e ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT=2181 \
confluentinc/cp-zookeeper:latestThen install and start Kafka
docker run -d \
--name kafka \
-p 9092:9092 \
--link zookeeper:zookeeper \ # link ZooKeeper container
-e KAFKA_BROKER_ID=1 \
-e KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT=zookeeper:2181 \ # connect to ZooKeeper
-e KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://localhost:9092 \ # c countainer outside ip address
-e KAFKA_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092 \ # container inside ip address
wurstmeister/kafka:latestIt will be installed automatically after a while.
$ docker pull wurstmeister/kafka
Using default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from wurstmeister/kafka
42c077c10790: Pull complete
44b062e78fd7: Pull complete
b3ba9647f279: Pull complete
10c9a58bd495: Pull complete
ed9bd501c190: Pull complete
03346d650161: Pull complete
539ec416bc55: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:2d4bbf9cc83d9854d36582987da5f939fb9255fb128d18e3cf2c6ad825a32751
Status: Downloaded newer image for wurstmeister/kafka:latest
docker.io/wurstmeister/kafka:latestIn web scraping, we use a Python environment and install the Kafka library
pip install kafka-python- Key Steps:
- Scrapers Produce Data
from kafka import KafkaProducer
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092')
def crawl(url):
html = requests.get(url).text
producer.send('raw_data', html.encode('utf-8'))- Cleaning Services Consume Data
from kafka import KafkaConsumer
consumer = KafkaConsumer('raw_data', bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092')
for message in consumer:
raw_data = message.value.decode('utf-8')
clean_data = process(raw_data) # 数据清洗函数
# 将清洗后的数据发送到新主题
producer.send('clean_data', clean_data.encode('utf-8'))- Example of Cleaning Logic
def process(raw_data):
# 1. remove HTML tag
clean_text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', raw_data)
# 2. extract struct data
data = extract_info(clean_text)
# 3. data validation
if not validate(data):
return None
# 4. format convert
return format_data(data)Now, let’s introduce the practical use of Kafka with a web scraping example
import requests
from kafka import KafkaProducer
import time
# Initialize Kafka producer (connect to Kafka cluster)
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092'])
def crawl_example(url):
try:
response = requests.get(url, timeout=10)
if response.status_code == 200:
# Extract raw page data (HTML) and URL
raw_data = {
"url": url,
"html": response.text,
"crawl_time": time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
}
# Send to Kafka's raw_page_topic (value needs to be converted to bytes)
producer.send(
"raw_page_topic",
value=str(raw_data).encode('utf-8')
)
print(f"Crawled and sent: {url}")
else:
# Crawling failed, send to error_log_topic
error_msg = f"Crawling failed, status code: {response.status_code}, URL: {url}"
producer.send("error_log_topic", value=error_msg.encode('utf-8'))
except Exception as e:
error_msg = f"Crawling exception: {str(e)}, URL: {url}"
producer.send("error_log_topic", value=error_msg.encode('utf-8'))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Crawl example.com and its sub-pages (example URL list)
urls = [
"https://globalnews.ca/national/",
"https://www.ctvnews.ca/",
"https://nationalpost.com/"
]
for url in urls:
crawl_example(url)
time.sleep(1) # Control crawling frequency to avoid triggering anti-crawling measures
producer.flush() # Ensure messages are sent completelyThe above code stores the crawled data into a topic.
Then, other consumers, i.e., data cleaning programs, can obtain data from the producer’s topic. Here, multiple consumers can consume the data produced by the producer simultaneously. That is, Kafka naturally supports distributed scraping systems well.
from kafka import KafkaConsumer, KafkaProducer
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import json
import time
# Initialize consumer (consume raw data) and producer (send cleaned data)
consumer = KafkaConsumer(
"raw_page_topic",
bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092'],
group_id="data_cleaner_group"
)
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092'])
def clean_raw_data(raw_data_str):
try:
raw_data = eval(raw_data_str) # Use json.loads in real scenarios
html = raw_data["html"]
url = raw_data["url"]
# Parse HTML, extract title and content (using example.com as example)
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
title = soup.title.text if soup.title else "No title"
content = soup.get_text().strip()[:500] # Take first 500 characters
# Structure cleaned data
cleaned_data = {
"url": url,
"title": title,
"content": content,
"clean_time": time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
}
return cleaned_data
except Exception as e:
print(f"Cleaning failed: {e}")
return None
for msg in consumer:
raw_data_str = msg.value.decode('utf-8')
cleaned_data = clean_raw_data(raw_data_str)
if cleaned_data:
# Send to cleaned_data_topic
producer.send(
"cleaned_data_topic",
value=json.dumps(cleaned_data).encode('utf-8')
)
print(f"Cleaned and sent: {cleaned_data['url']}")There are many advantages to introducing Kafka middleware in web scraping.
- Improve System Fault Tolerance
- If the cleaning service fails, Kafka can retain data to avoid data loss.
- After fault recovery, the cleaning service can continue consuming data from where it left off.
- Support Multi-Stage Processing
- Cleaning logic can be split into multiple independent services (such as word segmentation, deduplication, classification), connected in series through Kafka topics.
- Data Reuse and Auditing
- Raw data can be retained in Kafka for a certain period, facilitating backtracking and reprocessing.
- Multiple consumer groups can read data from the same topic simultaneously to achieve cleaning or analysis for different purposes.
By combining Kafka’s high throughput with data cleaning’s quality control, web scraping systems can handle massive amounts of data while ensuring data accuracy and availability.
